Implantation Bleeding vs. Period: Signs, Symptoms, and Key Differences
Noticing light spotting or unexpected bleeding can be confusing, especially if you’re trying to conceive or unsure whether your period is starting. Implantation bleeding occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterus lining, often causing light spotting. Because it happens close to when a period is expected, many people struggle to differentiate between implantation bleeding vs. period.
Understanding the differences between these two types of bleeding can help you determine whether you’re experiencing an early sign of pregnancy or just your regular menstrual cycle. Let’s explore what implantation bleeding looks like, when it occurs, and how to tell if it’s implantation bleeding or a period.
What is Implantation Bleeding?
Implantation bleeding is light spotting that occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining, also called the endometrium. This process happens approximately 7 to 14 days after fertilization. As the embryo burrows into the uterus, small blood vessels can break, leading to mild spotting. Though this bleeding is harmless and temporary, it can cause confusion since it often appears around the time a person expects their period.
When Does Implantation Bleeding Occur?
Implantation bleeding typically happens around 10 to 14 days after ovulation, usually a few days before a missed period. Because of its timing, many people mistake it for an early or light period. If you experience light spotting before your expected period, it might be implantation bleeding rather than menstruation. You can use our “Advanced Ovulation Calculator” to better track ovulation, implantation, and other important dates related to your menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Implantation Bleeding vs. Period: Key Differences
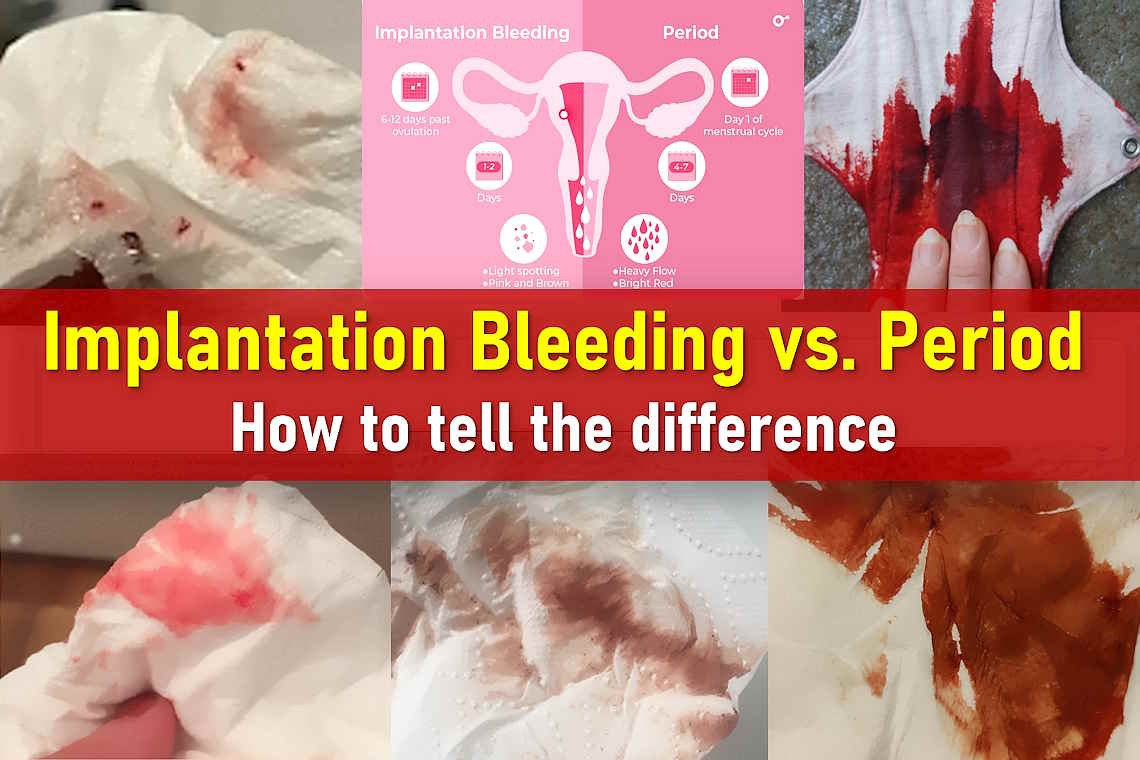
While implantation bleeding and periods share some similarities, there are crucial differences in flow, color, duration, and symptoms.
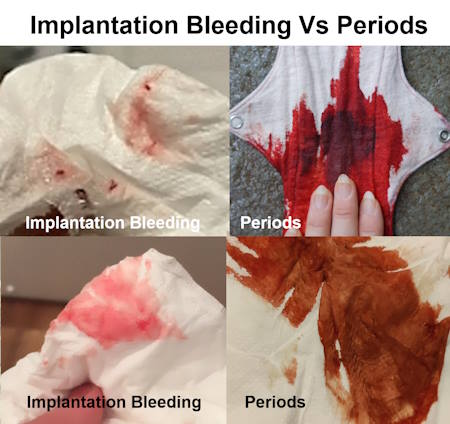
- Flow: Implantation bleeding is usually very light—often just spotting visible when wiping. A menstrual period, on the other hand, starts light but progresses to a heavier flow.
- Color: Implantation bleeding tends to be light pink, rust-colored, or brown, whereas menstrual blood is typically bright or dark red.
- Consistency: Period blood is often thick and may contain clots, while implantation bleeding is thinner and does not include clots.
- Cramping: Some people experience mild cramping with implantation bleeding, but it is much lighter and shorter than period cramps, which can be intense and prolonged.
- Timing: Implantation bleeding happens around days 20 to 24 of a typical 28-day cycle, while menstrual bleeding starts at the beginning of the cycle.
- Duration: Implantation bleeding lasts a few hours to a couple of days, whereas a period typically lasts 2 to 7 days.
- Clotting: Period blood often includes clots, but implantation bleeding does not cause the shedding of uterine lining, so clots are not present.
Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle to Identify Implantation Bleeding
Keeping track of your menstrual cycle can help you distinguish between implantation bleeding and your period. If you’re new to tracking, start by noting:
- Cycle length: Count the days from the first day of your period to the first day of your next period.
- Ovulation: Ovulation typically occurs 14 days before your next period. In a 28-day cycle, ovulation happens around day 14.
- Irregular cycles: If your periods are irregular, using ovulation tests or tracking symptoms like cervical mucus changes may help determine when you ovulate.
When to Take a Pregnancy Test
If you suspect implantation bleeding, the best time to take a pregnancy test is one week after a missed period. Pregnancy tests detect human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone that increases after implantation. Testing too early—during implantation bleeding—may result in a negative test because hCG levels are still low.
Will a Pregnancy Test Be Positive During Implantation Bleeding?
Since implantation bleeding occurs before a missed period, most pregnancy tests will not detect pregnancy at this stage. hCG production begins only after the fertilized egg fully implants, and it rises each day. For accurate results, wait until your period is late before testing.
By understanding the difference between implantation bleeding and period, you can better interpret early pregnancy signs and decide when to take a pregnancy test.
Other Possible Causes of Vaginal Bleeding
Bleeding outside of a normal period can happen for a variety of reasons, including pregnancy-related and non-pregnancy-related causes. While some cases are harmless, others may indicate an underlying condition that requires medical attention.
Pregnancy-Related Causes of Bleeding
Bleeding during pregnancy is relatively common, affecting about 15% to 25% of pregnancies. In early pregnancy, the cervix undergoes changes and develops more blood vessels, which can make light spotting more likely—especially after sex or a pelvic exam. However, other potential causes of bleeding during pregnancy include:
- Infections: Certain vaginal or cervical infections may lead to light spotting.
- Early pregnancy loss (miscarriage): Bleeding can sometimes be an early sign of miscarriage, especially if accompanied by severe cramping.
- Ectopic pregnancy: This occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube, which can cause bleeding and severe pain.
- Cervical inflammation: An inflamed cervix may bleed more easily.
- Placental issues: Conditions such as placenta previa or placental abruption can cause bleeding later in pregnancy.
- Preterm labor: Bleeding along with contractions before 37 weeks of pregnancy could be a sign of early labor.
Other Causes of Vaginal Bleeding
In addition to pregnancy-related reasons, other medical conditions and hormonal factors can cause unexpected vaginal bleeding:
- Ovulation bleeding: Some women experience light spotting during ovulation due to hormonal fluctuations. This typically lasts one to two days.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A hormonal disorder that affects ovulation and often leads to irregular or unpredictable periods.
- Cervicitis: Inflammation of the cervix, often due to a sexually transmitted infection (STI) like chlamydia or gonorrhea, can cause spotting after sex or between periods.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A complication of untreated STIs that causes inflammation in the reproductive organs, sometimes leading to irregular bleeding.
- Uterine or cervical polyps and fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus or cervix can cause spotting between periods or after intercourse.
- Birth control: Hormonal contraceptives, particularly low-dose pills, may cause breakthrough bleeding between periods.
- Thyroid disorders: An underactive or overactive thyroid can affect hormone levels, leading to irregular cycles.
- Endometrial cancer: Abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially postmenopausal bleeding, can sometimes be an early sign of uterine cancer.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
While implantation bleeding is harmless and does not require treatment, unexpected vaginal bleeding should always be evaluated by a healthcare provider, especially if you are pregnant or suspect pregnancy. A doctor can help determine whether the bleeding is normal or requires further investigation.
It’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding that requires changing a tampon or pad every hour
- Menstrual bleeding that lasts longer than seven days
- Menstrual cycles that are consistently shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Unexplained pelvic or abdominal pain unrelated to your period
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Does Implantation Bleeding Look Like?
Implantation bleeding is typically light spotting rather than a full flow. It often appears as pink, light red, or brown discharge. Unlike a period, it does not contain clots and is much lighter in consistency.
How Long Does Implantation Bleeding Last?
Implantation bleeding typically lasts anywhere from a few hours to two days. In rare cases, it may last slightly longer, but it is generally much shorter than a regular period.
Can You Have Implantation Bleeding After a Missed Period?
Implantation bleeding typically occurs before a missed period. If you experience light bleeding after missing your period, it may be due to other causes such as hormonal changes or early pregnancy spotting. Taking a pregnancy test can help confirm whether you are pregnant.
Is Brown Discharge Before a Period a Sign of Implantation Bleeding?
Brown discharge before a period could be implantation bleeding, especially if it is light and short-lived. However, brown discharge can also be due to hormonal changes, ovulation spotting, or old blood clearing out from a previous cycle.
Does Implantation Bleeding Have Cramps?
Some women experience mild cramping with implantation bleeding, but it is usually much lighter and shorter than typical menstrual cramps. Period cramps are usually more intense and last longer.
Can a Pregnancy Test Be Positive During Implantation Bleeding?
Since implantation bleeding happens before enough pregnancy hormones have built up, a pregnancy test may still show negative at this stage. For the most accurate results, take a test about one week after your missed period.
Can You Have Implantation Bleeding and Still Get a Period?
Implantation bleeding is different from a period. If you experience light spotting followed by a regular period, the spotting may have been due to hormonal changes rather than implantation. However, if the bleeding stops and no period follows, taking a pregnancy test can help confirm pregnancy.
Summary
Implantation bleeding occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining, leading to light spotting that is often pink or brown. This usually happens around days 20 to 24 in a typical 28-day menstrual cycle.
In contrast, menstrual bleeding is part of a normal cycle and involves a heavier flow of bright or dark red blood. If you suspect pregnancy, the best way to confirm is by taking a pregnancy test about one week after a missed period.
If you experience unexpected or unusual bleeding, it’s always a good idea to consult a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying conditions.